Kenya's digital economy has shifted from policy drafting to active implementation. As of January 2026, the country executes the National Digital Master Plan 2022-2032 with a specific focus on the Green Digital Economy, data sovereignty, and infrastructure expansion.
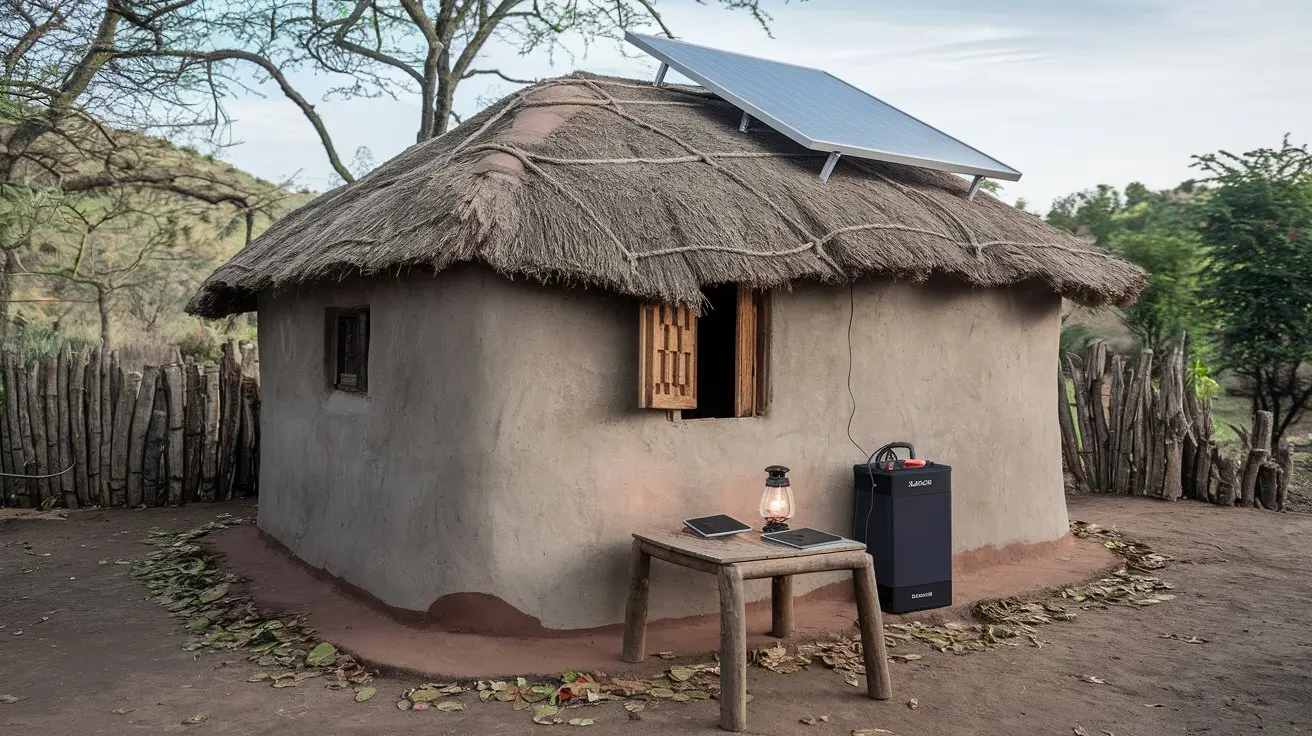

The government and private sector now prioritize practical application over infrastructure rollout.
Businesses utilize the expanded fiber network for cloud computing, while the public sector focuses on digitizing the remaining manual services. We analyzed the current state of this transformation based on data from Q4 2025 and Q1 2026.
Key Trends Defining Kenya's Digital Economy in 2026

Stakeholders in finance, agriculture, and government identify three primary trends: the operationalization of AI, the enforcement of data laws, and the integration of green technology.
1. Artificial Intelligence in Public Services
Artificial Intelligence (AI) now handles triage and resource allocation in key sectors. County hospitals in Nairobi and Kisumu use AI-driven diagnostics to screen patients before they see a doctor. This reduces wait times in Level 4 facilities.
The agricultural sector uses similar technology. Projects like the Strathmore University Mini-Weather Stations provide real-time soil data to farmers in Busia. This data allows farmers to adjust fertilizer application based on current moisture levels rather than historical averages.
2. The Green Digital Economy

Digitalization in 2026 links directly to climate action. Konza Technopolis operates its primary data center using renewable geothermal energy. This move aligns with the Ministry of ICT's directive to reduce the carbon footprint of digital infrastructure.
International partners like GIZ support this shift through the Digital Transformation Center (DTC) Kenya. They fund initiatives that combine digital skills training with environmental sustainability.
3. Data Protection and Compliance
The Office of the Data Protection Commissioner (ODPC) strictly enforces the Data Protection Act. Kenyan businesses now require clear consent protocols to collect user data. This enforcement builds trust in local e-commerce platforms, as consumers know they have legal recourse regarding their private information.
4. Gig Economy Regulation
Platform work (ride-hailing, food delivery, online freelancing) employs a significant portion of the workforce. The focus in 2026 is on "Fairwork" principles. New regulations ensure platform workers receive transparent contracts and fair pay, moving the sector away from informal labor practices.
Infrastructure: 5G and Broadband Status

Connectivity projects have moved past the pilot phase. Airtel Kenya and Safaricom provide 5G coverage in all county headquarters. High-speed internet allows businesses outside Nairobi to access centralized cloud services without latency issues.
The government's "Digital Superhighway" project continues to lay fiber optic cables. This expansion connects sub-urban market centers to the national grid, allowing SMEs in these areas to compete with urban counterparts.
Government Services and the Master Plan
The National Digital Master Plan 2022-2032 guides public sector activities. The mid-term review indicates progress in two specific areas: the GovStack initiative and digital skilling.
Public Service Digitization (eCitizen)
The eCitizen platform hosts over 20,000 government services. Citizens renew licenses, apply for passports, and pay land rates online. The "GovStack" approach standardizes these applications, meaning different government agencies use compatible systems to share data securely.
Digital Literacy and Skilling
The Jitume Program and the Ajira Digital Program train youth in digital skills. These initiatives target the skills gap, ensuring the workforce can operate the tools introduced by foreign investors and local tech startups.
Economic Impact on SMEs and Finance
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) contribute approximately 24% of Kenya's GDP. Digital tools help these businesses reduce operational costs.
Fintech Integration: I&M Bank and other lenders offer APIs that integrate directly with SME inventory systems. This allows banks to lend based on real-time cash flow data rather than collateral, fixing a long-standing credit access problem.
Mobile Money Evolution: M-Pesa remains the dominant payment rail. However, usage has shifted from simple transfers to complex financial products. Users now access insurance, government bonds (M-Akiba), and global investment funds directly through mobile wallets.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the pillars of Kenya's Digital Master Plan?
- The plan relies on four pillars: Digital Infrastructure, Digital Services and Data Management, Digital Skills, and Digital Innovation/Entrepreneurship. code Code
- How does the Data Protection Act affect Kenyan businesses?
- Businesses must register as data controllers or processors. They must obtain explicit consent before collecting personal data and report any data breaches to the ODPC within 72 hours.
- What is the Green Digital Economy in Kenya?
- This refers to using digital technologies to achieve climate goals, such as powering data centers with renewable energy and using IoT sensors to monitor environmental conditions.
About the Research
This report compiles data from the CollinsMeroka Digital Marketing Agency analysis of the 2026 digital landscape. We cross-referenced our findings with reports from:
About the Author

Collins Meroka is a Digital Marketing Consultant with over a decade of experience applying psychological principles to digital marketing campaigns across Kenya. He holds a degree in Telecommunications... [Read more]